
How to Protect Your Child’s Hearing
This page contains affiliate links for which we may be compensated
Last updated: July, 2025
Hearing is a precious sense that plays a crucial role in a child’s development, communication, and overall well-being. As parents, it’s our responsibility to ensure that we take every measure to protect our child’s hearing. In this article, we will explore the importance of safeguarding your child’s hearing and provide practical tips on how to do so.
Understanding the Importance of Child’s Hearing
Before delving into protective measures, it’s essential to recognize the significance of your child’s hearing. Hearing is critical for language development, social interaction, and cognitive growth. Impaired hearing can have lasting effects on a child’s learning ability and emotional well-being. Hence, safeguarding your child’s hearing should be a top priority.
Types of Hearing Damage
Hearing damage can take various forms, and it’s crucial to be aware of the different types to understand the potential risks to your child’s hearing. Here are the most common types of hearing damage:
Tinnitus – an ongoing ringing sound in the ears.
Hyperacusis – diminished tolerance for loud noises and enhanced sensitivity to everyday noises.
Dysacusis – sound distortion.
Diplacusis – an irregular difference in the ears’ perception of pitch.
Limiting Noise Exposure
Noise-induced hearing loss is a prevalent concern in children. To protect your child’s hearing, it’s important to limit their exposure to loud noises. Here are some tips:
- Monitor the volume of electronic devices, such as headphones and video games.
- Encourage your child to take breaks during activities that involve loud sounds.
- Be cautious at events with loud music, such as concerts or sporting events, and use ear protection when necessary.
Practice Safe Listening
Teach your child about safe listening habits from an early age:
- Show them how to adjust the volume on their devices to a safe level.
- Educate them about the 60/60 rule – listening at 60% of the maximum volume for no more than 60 minutes at a time.
- Encourage open communication, so your child can express any discomfort or concerns about their hearing.
Musical Instruments
Most people don’t usually associate wearing protective gear with playing an instrument, but that’s exactly what needs to be done. There are dangers to your child’s hearing associated with learning to play any instrument.
Piano
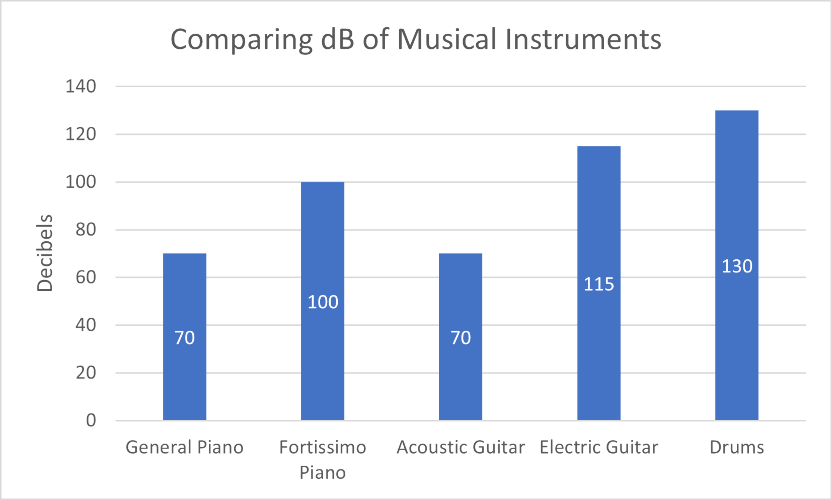
The piano is a versatile instrument known for its wide dynamic range. Its sound can range from soft and gentle to powerful and resonant, depending on how the musician plays. Typically, the decibel level of a piano falls within the following ranges:
- Soft Playing (pianissimo): 40-60 dB
- Moderate Playing (mezzo-forte): 60-80 dB
- Loud Playing (fortissimo): 80-100 dB
It’s important to note that digital pianos and acoustic pianos can vary in sound output, with digital pianos typically having a more consistent volume, while acoustic pianos may produce louder sounds when played forcefully.
Guitar
Guitars, whether acoustic or electric, produce sound through string vibrations. The decibel levels of a guitar can vary depending on the type, amplification, and playing style:
- Acoustic Guitar: 60-90 dB
- Electric Guitar (unplugged): 70-95 dB
- Electric Guitar (amplified): 85-120+ dB
Electric guitars can reach higher decibel levels when connected to amplifiers and effects pedals, making them suitable for rock and metal genres but requiring hearing protection in high-volume settings.
Drums
Drums are inherently loud instruments due to the impact and resonance of striking various components. Decibel levels for drum kits can be quite high, and they can vary significantly depending on the type of drums and the player’s technique:
- Acoustic Drum Kit: 90-130+ dB
- Electronic Drum Kit: 70-100 dB
Drummers are often exposed to the loudest sound levels in a band, making hearing protection vital to safeguard their hearing.
Types of Hearing Protection
To safeguard your child’s hearing in various situations, it’s essential to be aware of the types of hearing protection available. Choosing the right hearing protection for your child’s specific needs can significantly reduce the risk of hearing damage. Here are some common types of hearing protection:
Earplugs: Earplugs are small, soft devices that can be inserted into the ear canal to block out or reduce the intensity of sounds. There are disposable foam earplugs, reusable silicone earplugs, and custom-molded earplugs available. Custom-molded earplugs, made by a professional to fit your child’s ears precisely, provide the highest level of comfort and protection.
Earmuffs: Earmuffs, also known as noise-canceling headphones or ear defenders, are worn over the ears to create a seal that reduces incoming sound. They are especially effective for protecting against loud noises in industrial settings, at concerts, or during recreational activities like motorcycling. Child-sized earmuffs are designed to be comfortable and provide a snug fit.